# Gateway Configuration
| Deployment Manual | Version | Compiled by | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gateway Configuration | V1.0.0 | Wang Jiale | 2025.08.21 |
# Functional Introduction
- Service Proxy Functionality: Integrate target services into the gateway to provide unified proxy for plugin services
- Cross-Domain Solution: Automatically handle cross-domain request issues on the web frontend
- Request Standardization: Unified management of HTTP/HTTPS protocol conversion to eliminate duplicate project configurations
- Unified Authentication Center: Provide centralized identity authentication services for all sub-services
# General Gateway Configuration
- Go to the service homepage and click "Gateway Configuration"
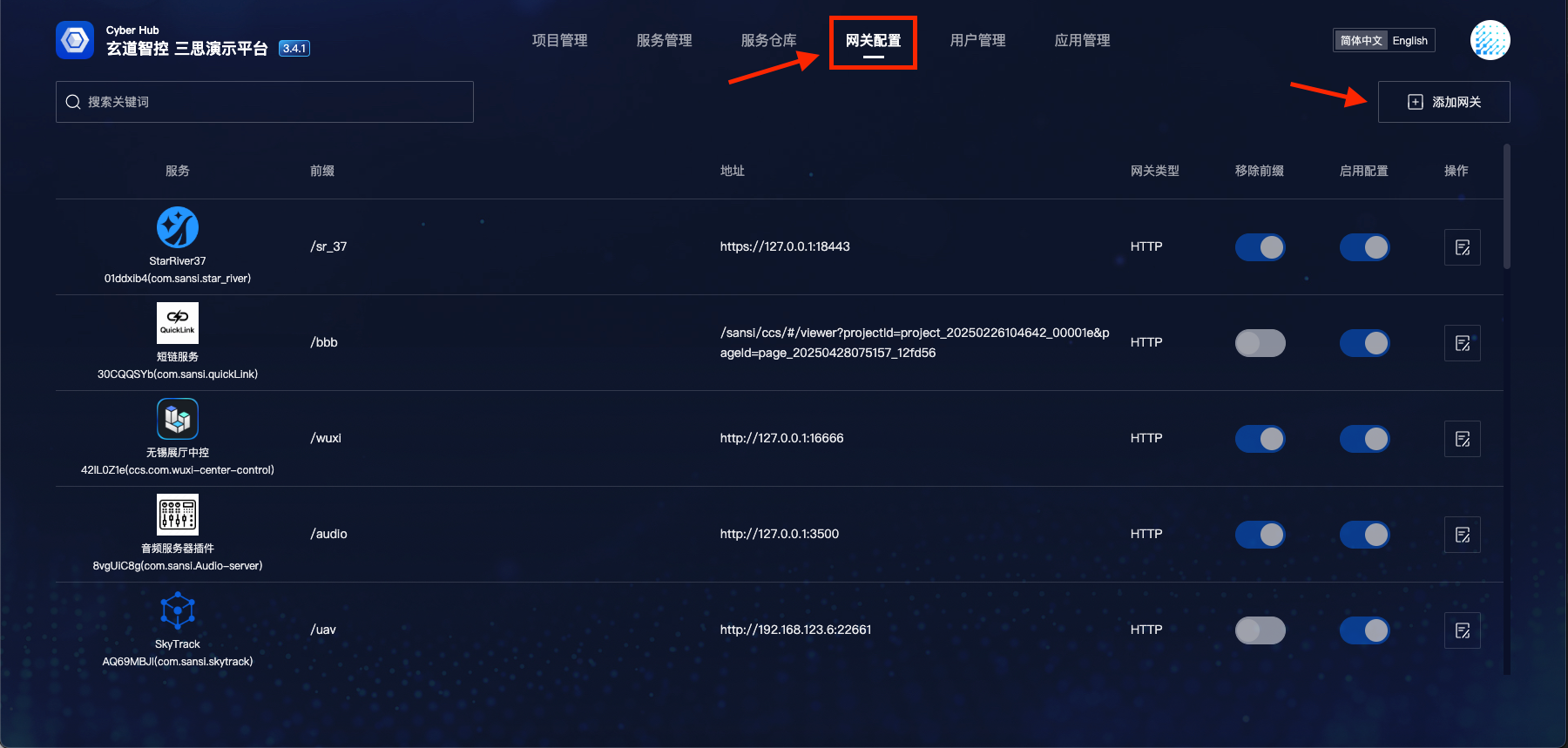
- Click "Add Gateway", select to add a gateway for the target service; for external services, you can select any downloaded plugin service
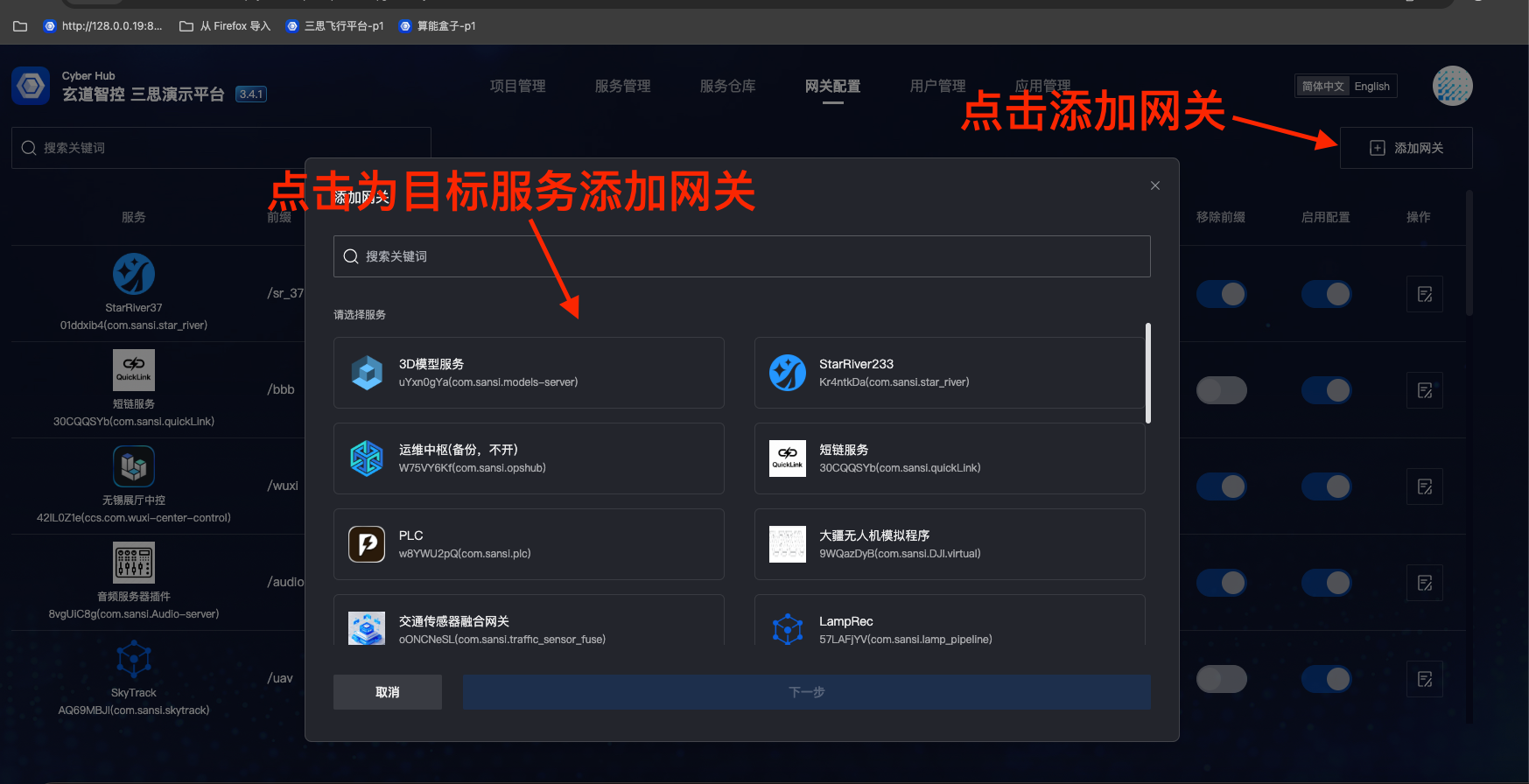
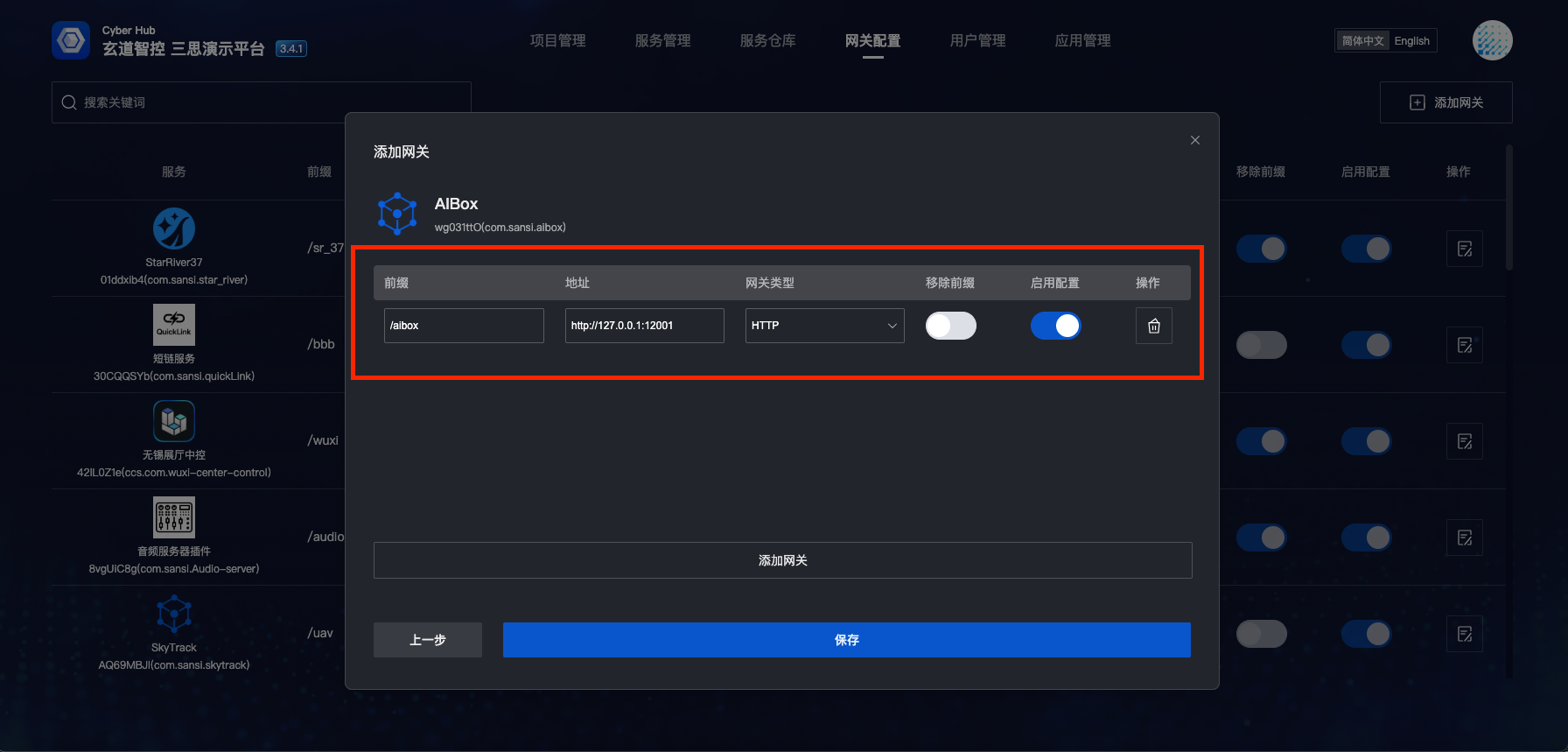
- Fill in gateway prefix, gateway address, gateway type, whether to remove prefix, whether to enable and other options, then click "Confirm"
- Gateway prefix is the path prefix after proxy, e.g., prefix
/aiboxforhttp://127.0.0.1:12001 - Accessing
http://127.0.0.1:1280/aiboxwill be proxied tohttp://127.0.0.1:12001, solving cross-domain issues and providing unified routing - Whether to remove prefix: If the proxied route address includes the prefix, select "Do not remove prefix"; if the proxied route does not include the prefix, select "Remove prefix"
- Whether to enable proxy: Determines if the proxy takes effect
- Gateway type: Select based on the type of proxied service (http, WebSocket)
- Gateway prefix is the path prefix after proxy, e.g., prefix
# Short Link Gateway Configuration
Short link gateway configuration converts long URLs into short, easy-to-remember links.
- Select a web address such as:
/sansi/ccs/#/viewer?projectId=project_20250226104642_00001e&pageId=page_20250428075157_12fd56 - Click "Add Gateway" and select "Short Link Gateway"
- Enter an easy-to-remember link in the prefix input box, such as:
/aaa - Click "Confirm"
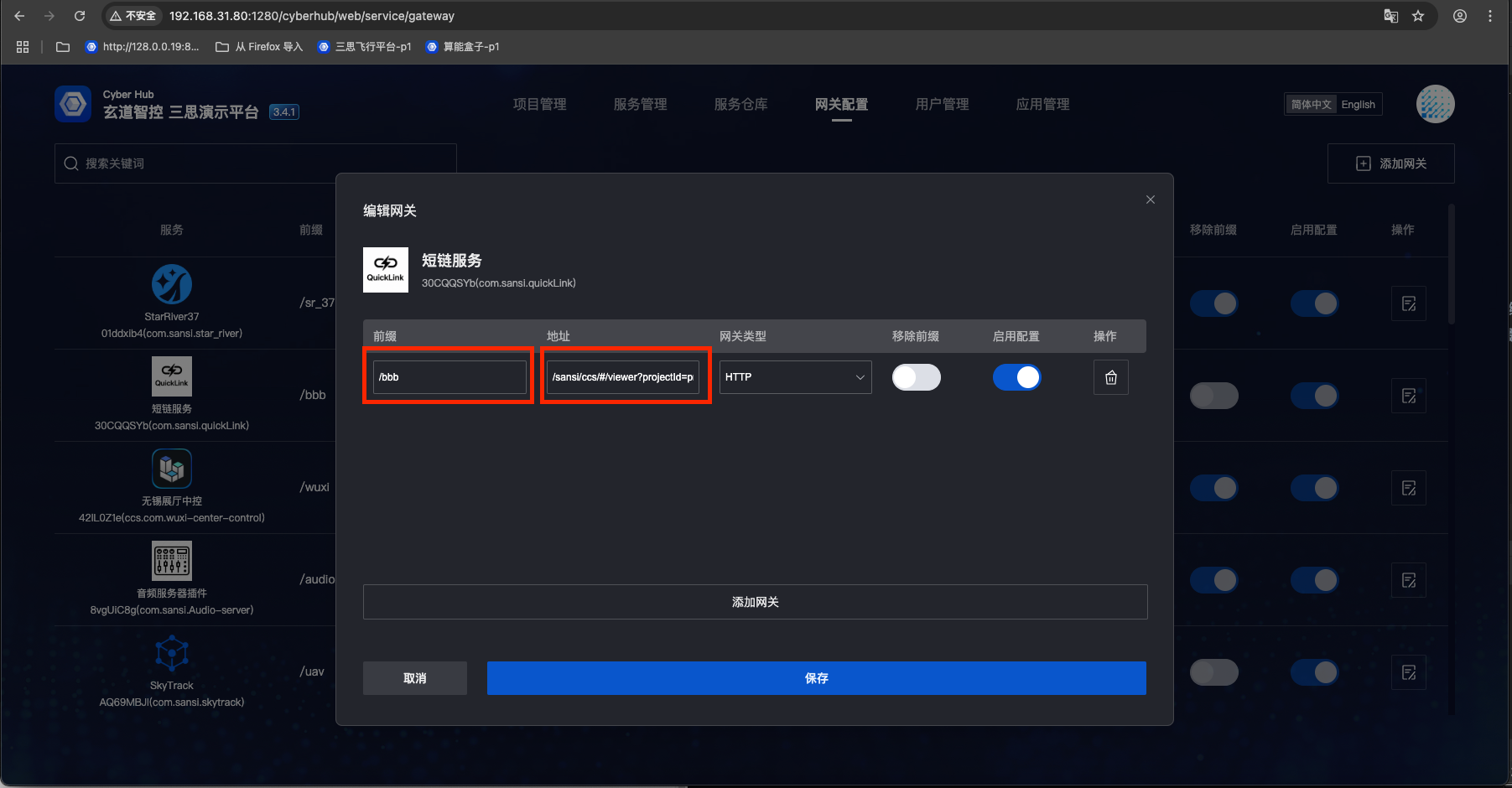
- Access: http://127.0.0.1:1280/aaa to reach the target service
# SR Gateway Configuration
- SR gateway configuration is the same as general configuration. Example configuration:
/star_riverhttps://sr.sansi.net:18400type: http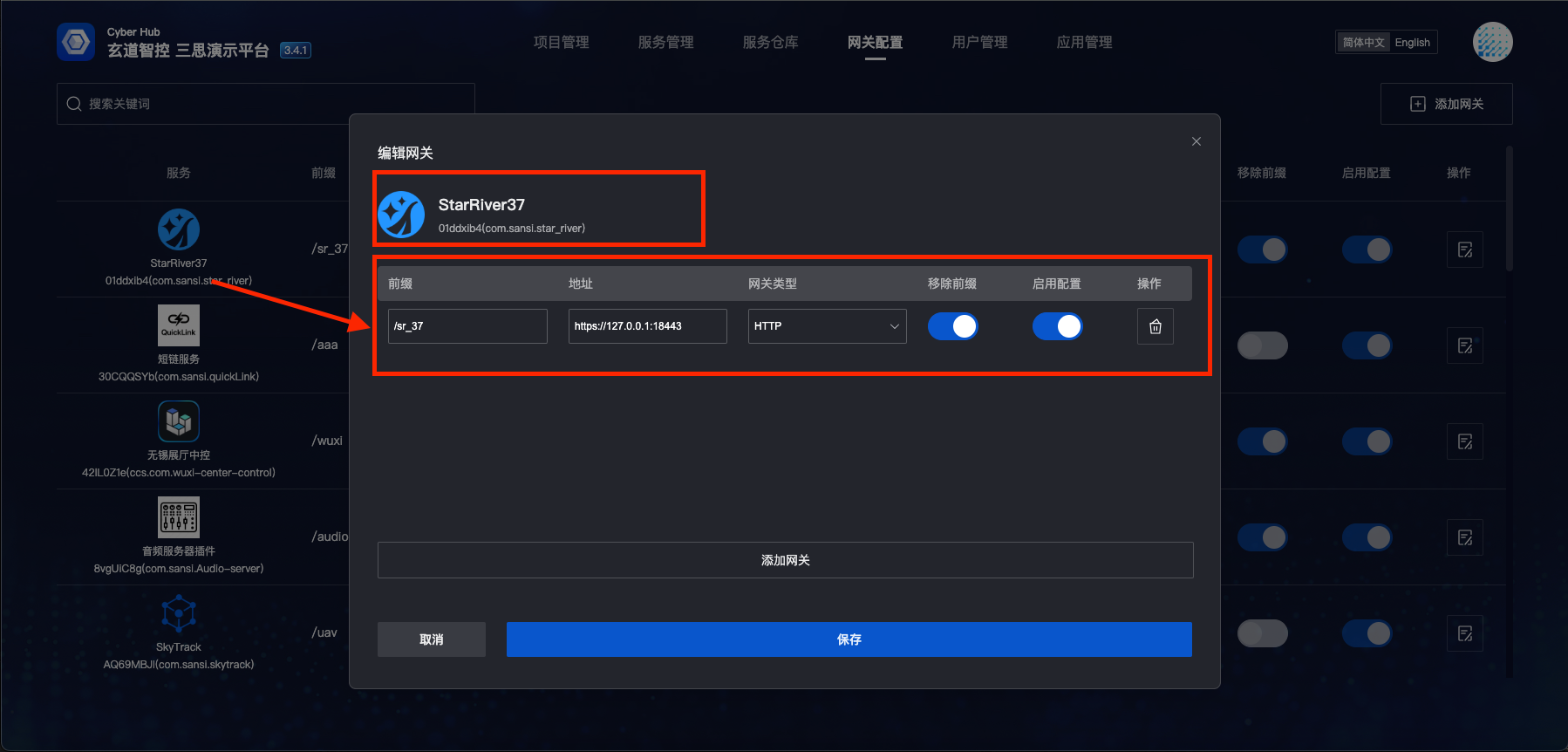
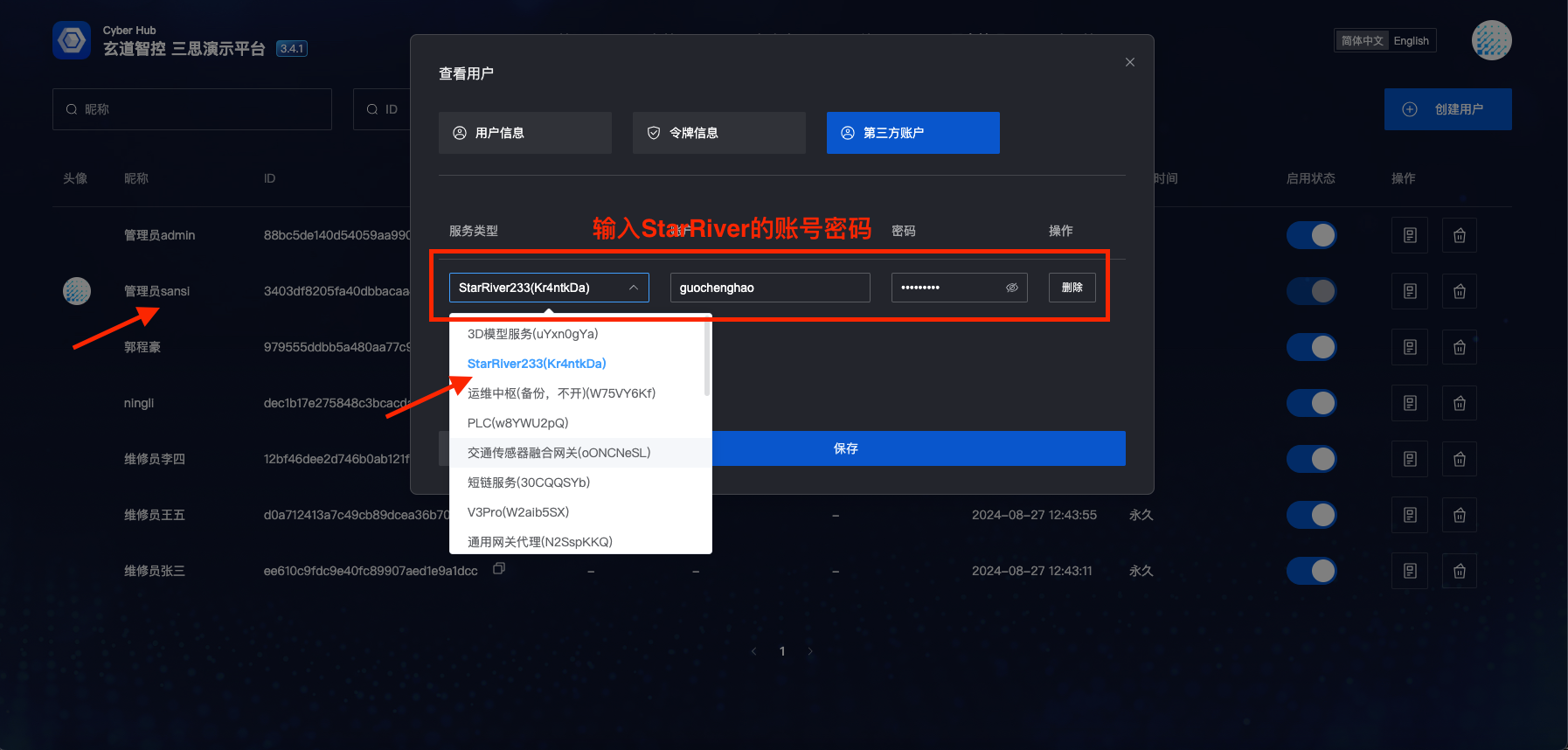
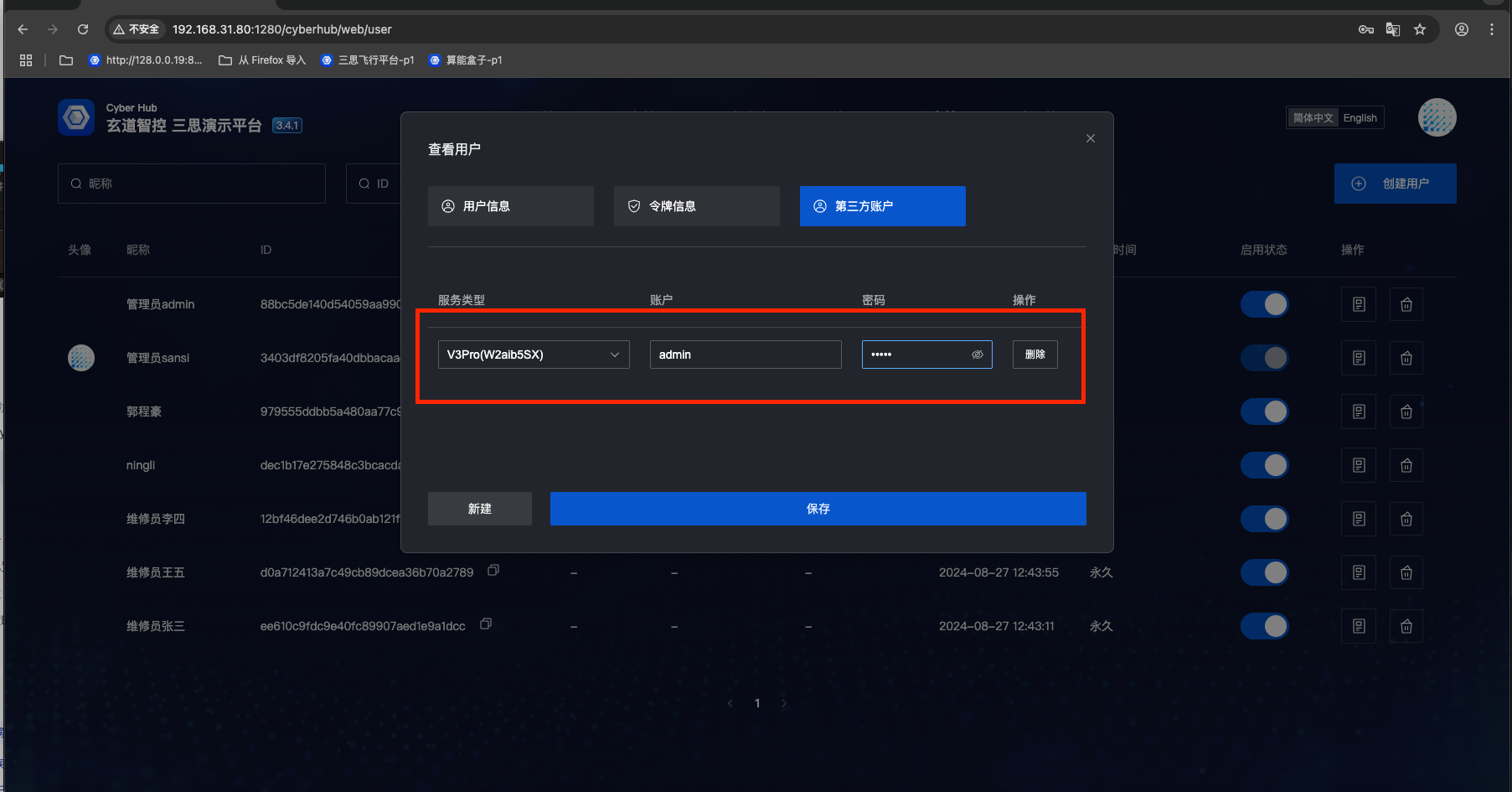
- SR requires account password binding. Steps are as follows:
- Select "User Management"
- Select a user
- Click "Edit" button
- Bind third-party account
- Select target SR application (there may be multiple SR applications in one project)
- Enter SR application account and password
- Click "Save"
# V3Pro Protocol Gateway Configuration
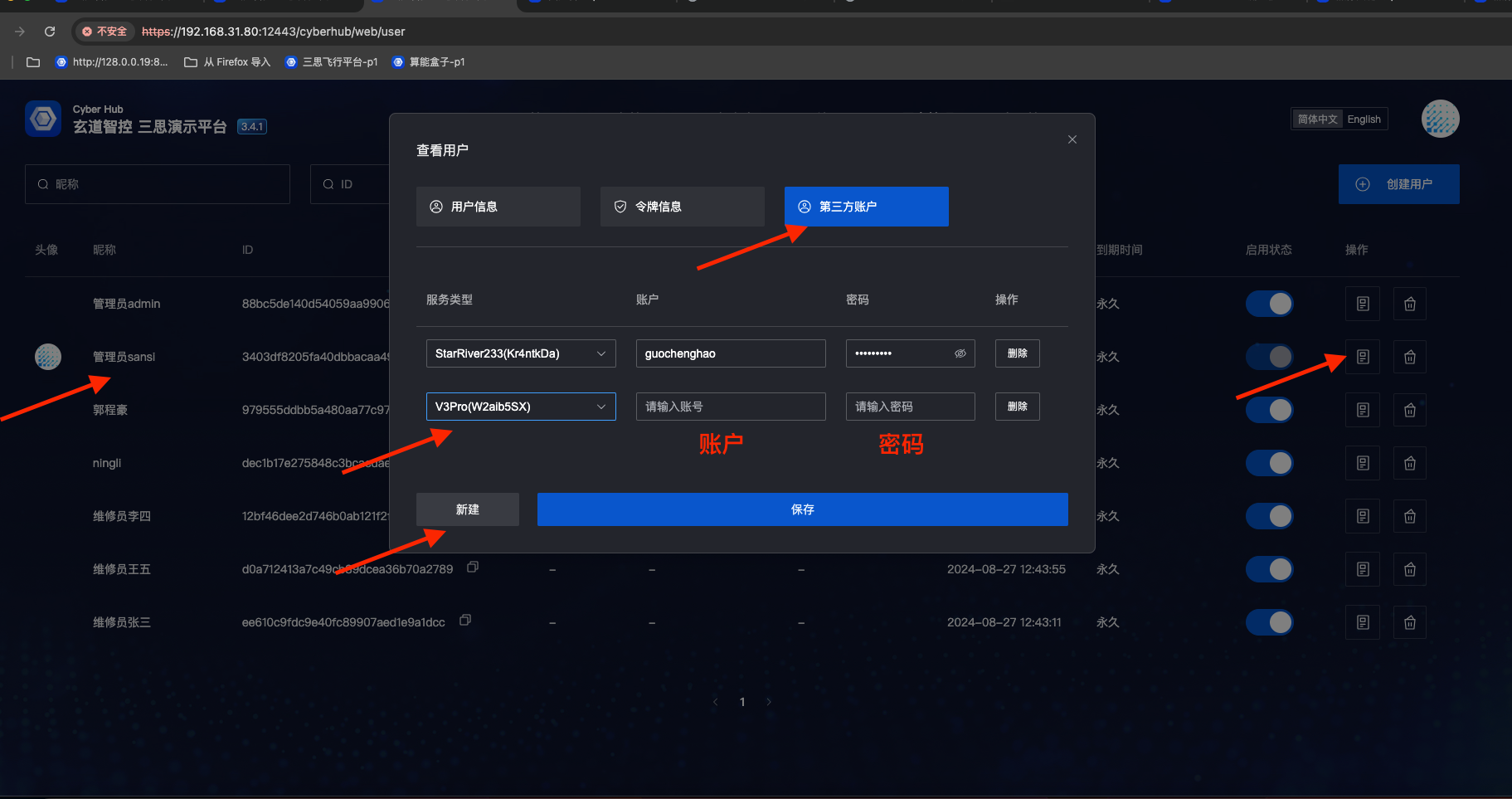
- V3Pro protocol gateway configuration is the same as SR configuration. Users also need to bind V3Pro service account and password. Steps are as follows:
- Select "User Management"
- Select a user
- Click "Edit" button
- Bind third-party account
- Select target V3Pro application (there may be multiple V3Pro applications in one project)
- Enter V3Pro application account and password
- Click "Save"
- Note that V3Pro gateway requires configuration of both http and WebSocket protocols
- http gateway example configuration:
/v3proApihttp://127.0.0.1:12409type: http - WebSocket gateway example configuration:
/v3proWsws://127.0.0.1:12410type: WebSocket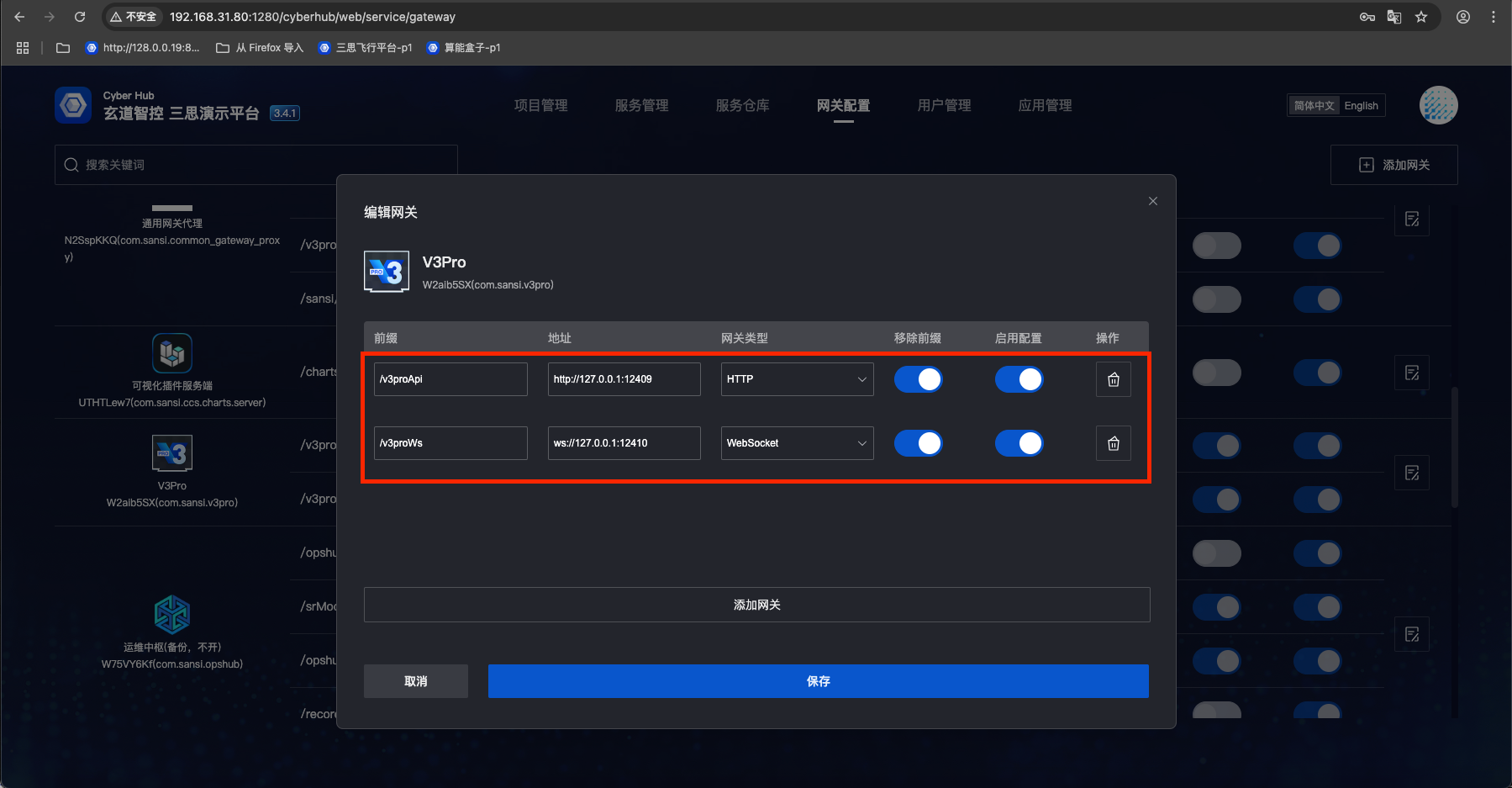
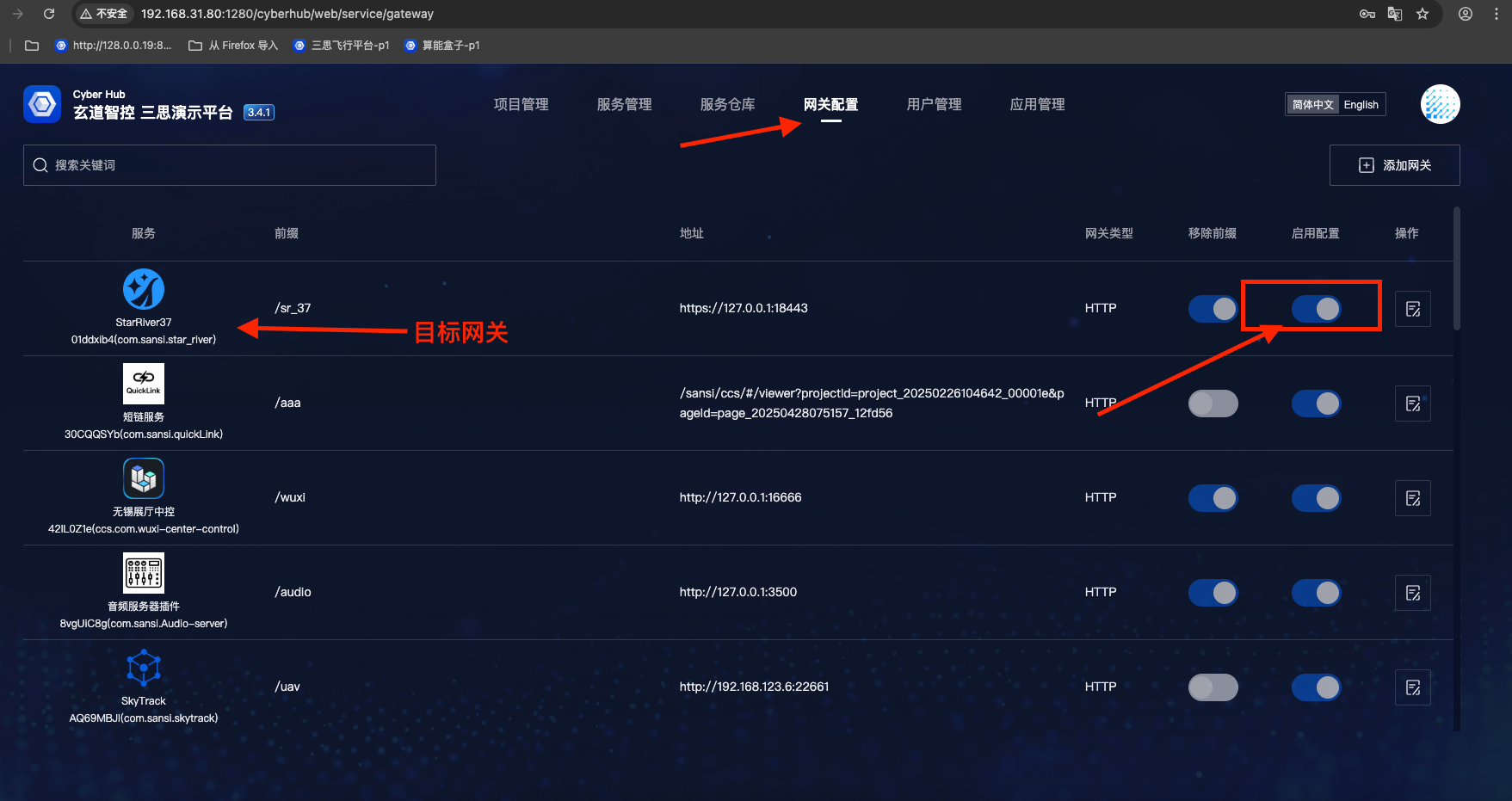
# Removing Gateway Configuration
- To disable gateway configuration while temporarily retaining it: Gateway Configuration => Select target gateway => Click "Enable Configuration" button => Disable the gateway
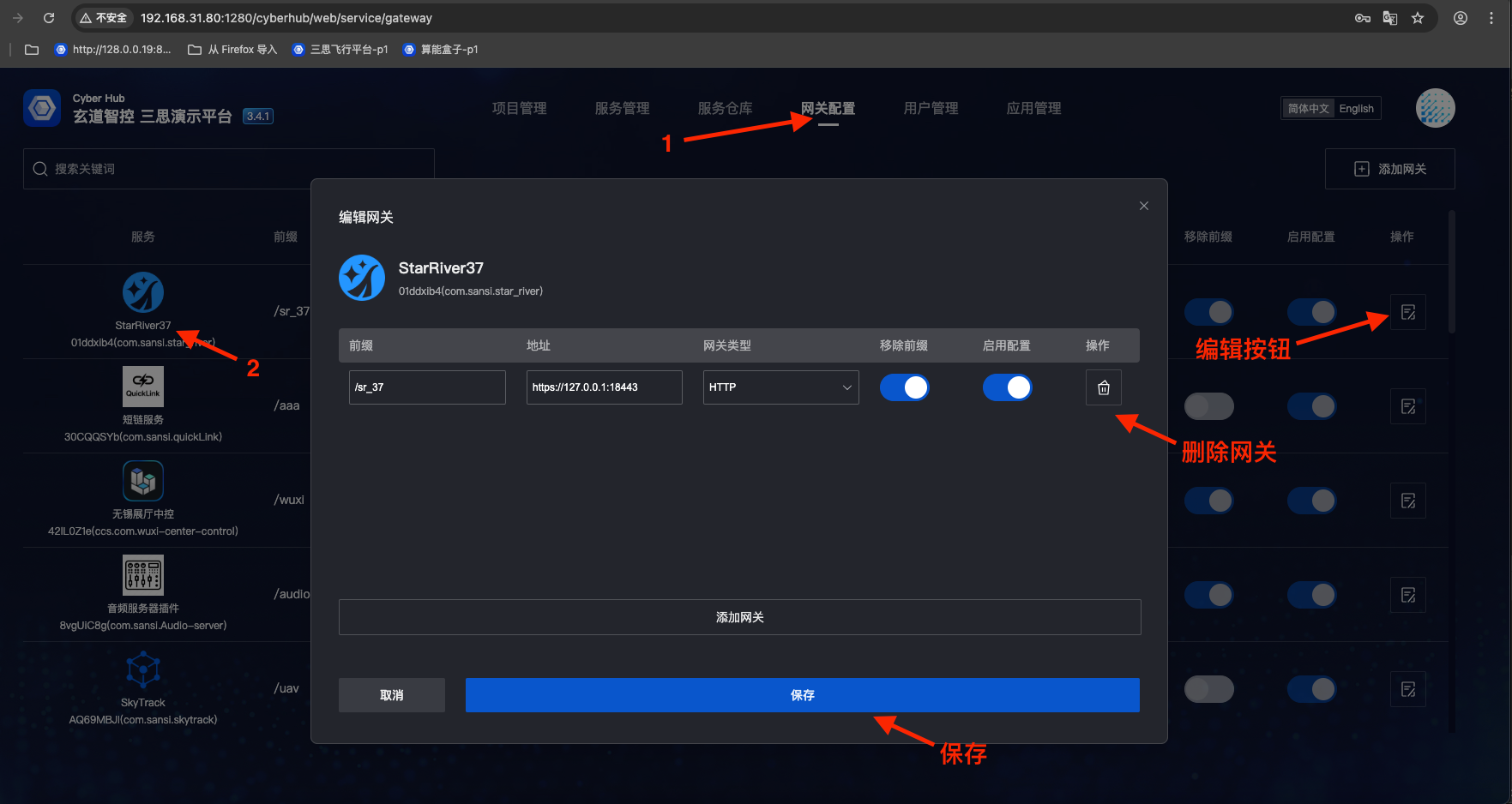
- To delete gateway configuration (permanently remove the configuration): Gateway Configuration => Select target gateway => Click "Edit" button => Click "Delete" button => Click "Save"
# Precautions
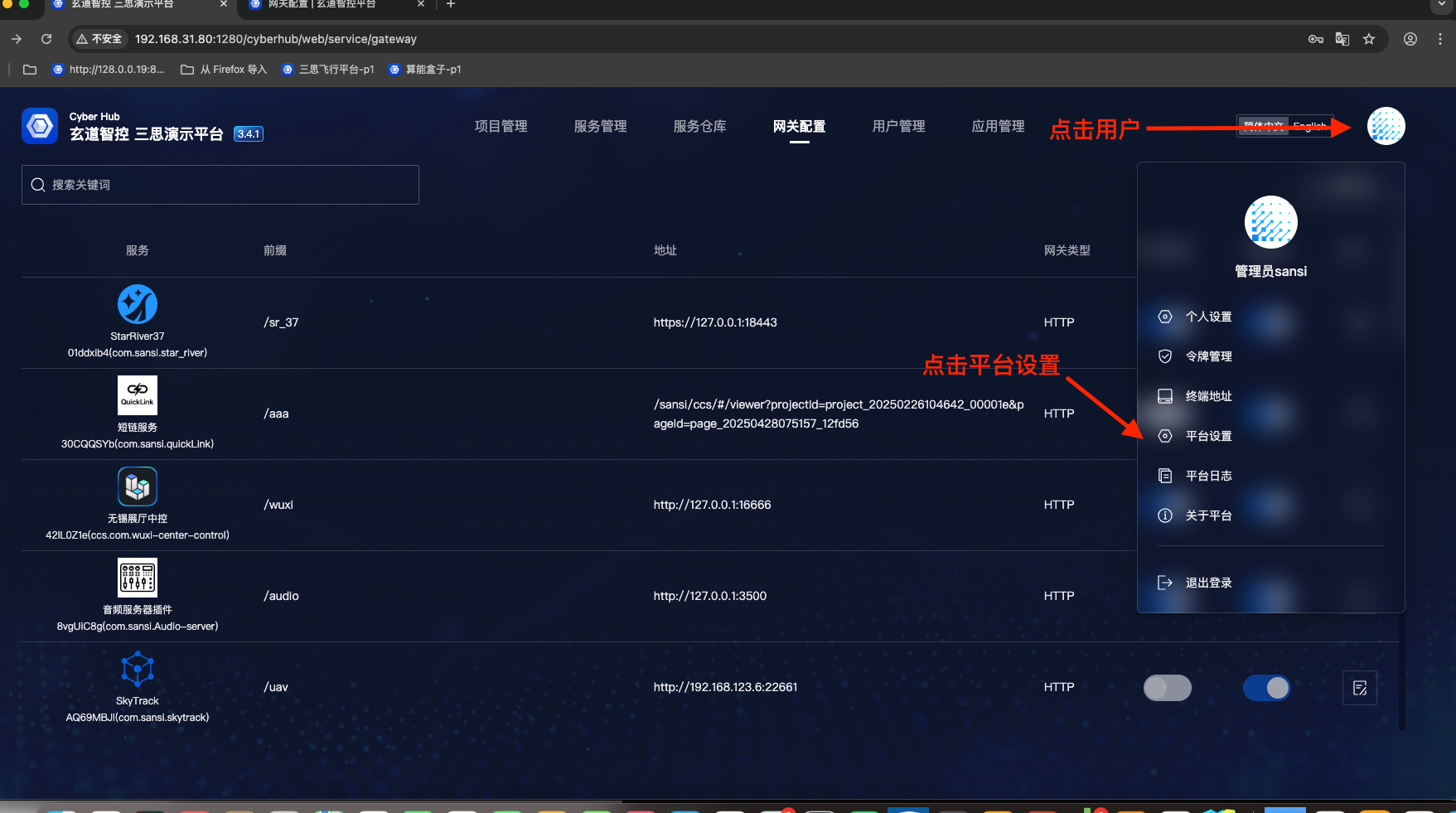
If the newly added gateway configuration does not take effect, please restart the platform software. Steps: Click user avatar => Click "Platform Settings" => Click "Save and Restart" button
# Gateway Principles
# 1. Basic Definition
A gateway is a protocol conversion and routing intermediary between different network systems, acting as a "network translator". In a microservice architecture, the gateway serves as the unified entry point for all external requests, implementing traffic scheduling and protocol adaptation.
# 2. Core Working Principles
- Traffic Proxy Mechanism
- After receiving client requests, the gateway forwards them to corresponding microservice instances through the built-in routing table
- Supports HTTP/HTTPS protocol conversion to eliminate protocol differences between services
- Typical proxy modes include:
- Forward proxy (hides client identity)
- Reverse proxy (protects server resources)
- Cross-Domain Solution
- Automatically adds CORS response headers (e.g., Access-Control-Allow-Origin)
- Uniformly handles OPTIONS preflight requests
- Authentication and Security
- Centralized identity authentication (e.g., JWT verification)
- Automatic login implemented through Cookie/Session synchronization
- Traffic encryption (SSL/TLS termination)